ApplicationContext Hierarchies
Spring MVC 설정에서 root-context와 servlet-context 계층 구조 및 역할에 대해 알아봅니다.
Spring MVC 설정 파일에서 설정을 하다 보면,
root-context 계층의 설정이 있고, servlet-context 계층의 설정 파일이 있다.
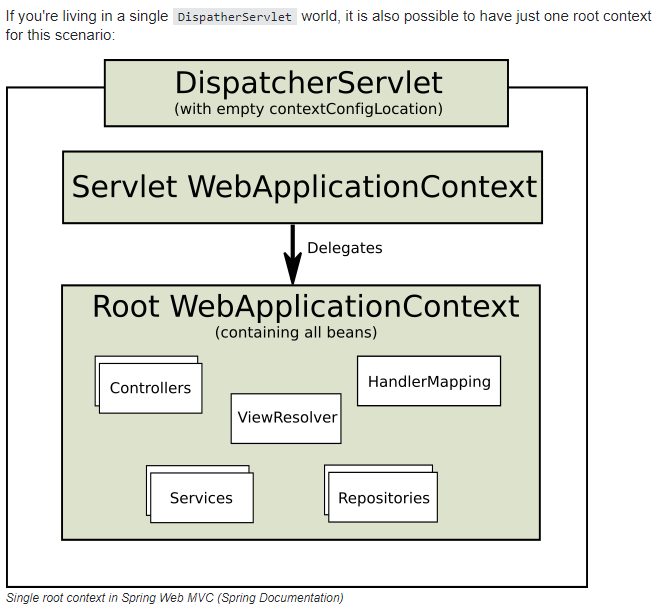
하지만 일반적인 경우 (1개의 dispatcher servlet) 에는, 두 설정 파일의 위치가 바뀌어도 큰 상관이 없음을 확인할 수 있었다.
각각의 기능을 파악하던 도중, Stack Overflow 에서 잘 정리해 둔 글을 발견했다.
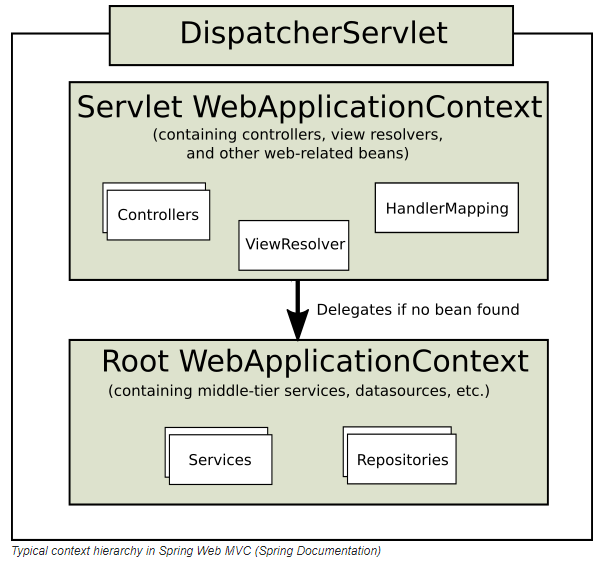
Spring's ApplicationContext provides the capability of loading multiple (hierarchical) contexts, allowing each to be focused on one particular layer, such as the web layer of an application or middle-tier services.
One of the canonical examples of using hierarchical ApplicationContext is when we have multiple DispatcherServlets in a web application and we're going to share some of the common beans such as datasources between them. This way, we can define a root ApplicationContext that contain all the common beans and multiple WebApplicationContexts that inherit the common beans from the root context.
In the Web MVC framework, each DispatcherServlet has its own WebApplicationContext, which inherits all the beans already defined in the root WebApplicationContext. These inherited beans can be overridden in the servlet-specific scope, and you can define new scope-specific beans local to a given Servlet instance.
이것도 읽어보세요